Description: If you have been in education long enough, many trends come and go. Today’s teachers are bombarded with trends, meeting content standards, yet reaching for what today’s students need. One teacher examines the evolving learning environment while focusing on the empowered learning of her students.
What are the ISTE standards for students?
Performance indicators for ISTE standards for students
Why use the ISTE Standards?
It is not just about changing the assignment, it is about a shift in teaching and pedagogy first. What you know is the content standards, what you do is the ISTE standards. It is student centered – not one specific answer every student gives. What students do is important. It requires thoughtful planning using technology and allows for more productivity and differentiation. It is about the learning and not the tools. Keep in mind SAMR (Substitute – function is the same as not using technology, Augmentation – adds more function, Modification – task is modified and redesigned, and Redefinition- new tasks not possible before technology). We are aiming for Redefinition.
1. Empowered Learner
“Student leverage technology to take an active role in the choosing, achieving and demonstrating competency in their learning goals, informed by the learning sciences.”
Setting personal learning goals
- What improvement so they want to make?
- Goals, reminder, track progress using an app, reflection of work towards a goal.
- Follow goals in google calendar on a mobile device
- Have them connect a learning goal and extension to help them meet the goal (Strict workflow, Memorize!, Easybib)
- Blogging, feedback/reflection
- Use a Google slide for a simple portfolio
- Single point rubrics to get feedback on improvements and what is great. (Template)
- Tools: Google slides, Google sites, Google docs, OneNote, Seesaw, Notability, Evernote, Blogger, Kidblog, Google Calendar
Customize learning/Demonstrate learning
- Student choice of digital tool in learning and demonstrating knowledge
- Rubric based upon learning goals not just the technology
- Digital storytelling – don’t let powerpoint be the only option.
- Learning menus/Learning stations – computer, lab, small group, teaching (students are a teacher and thoughtful listener), assessment, 9 or 12 box worksheet with choices (for example, choose 5 or complete a row)
- Jigsaw- teach each other
- Question they want to research
- Why are these statements incorrect? Why do people think they are correct?
- Apply content to new situation, make meaning out of new info
- Choice is more than a menu of options – what is wrong with the statements that I just wrote, what do I want to know, active learning (students still need structure).
- Tools: Skype, Hangouts, Twitter, Texting, Pinterest, LMS, Apps, G suite training, Skitch, Screencastify, Google Keep, Todoist, Edmodo, Instagram, YouTube, Symbaloo, Scratch, Google search. extension, Thinglink, Canva, Prezi, News feeds, Explain everything, Buncee
 .
.
2. Digital Citizen
Students recognize the rights, responsibilities and opportunities of living, learning and working in an interconnected digital world, and they act and model in ways that are safe, legal and ethical.
- Learning about websites http vs. https, evaluating websites
- CRAAP test
- Hoax sites
- Checking MLA to determine site authenticity
- Credible sourcing
- Digital identity posters
- Resources, discussions, looking at viewpoints in different countries
- Responsible use of language
- Fair use, copyright, plagiarism, citing sources
- Smithsonian learning lab for images
- Be internet awesome program and Interland app
- Search Google images for reuse
- Google yourself
- Google search challenges
- Learning how to search
- Google alerts
- CommonSense.org
- Your entire life is online
- Easybib.com – enter http to generate questions about site
3. Knowledge constructor
Students critically curate a variety of resources using digital tools to construct knowledge, produce creative artifacts and make meaningful learning experiences for themselves and others.
- Asking questions, using a search and search terms effectively, using databases,
- Evaluating a website
- Curating resources
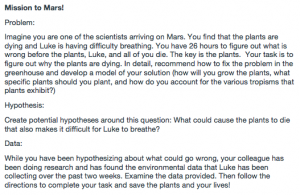
- PBL – projects that anchor the unit and use info and skills. Current events or videos that are important. Simulations, VR
- Learning targets- I can define…I can explain…I can explain how…
- What questions do you have about…. Can also rank order in groups then in class
- Jigsaw
- Create a video showing a practical application of what was learned
- Gallery walk, guided investigations
- Tools: I chart, KWL chart, Symbaloo, Google suite/wiki/LMS, Google expeditions, Pinterest, News feeds, Newsela, Biteable
4. Innovative Designer
Students use a variety of technologies within a design process to identify and solve problems by creating new, useful or imaginative solutions.
- Design thinking process: empathize (how to approach the challenge), define (the approach), ideate (what do we create), prototype (how do we build it), test (how do we prove and improve).
- Design Thinking Projects and Challenges
- Creation Tools
- Help students become innovative designers
- Use open ended questions for an activity, include ambiguity
- What if…? What could you do…? Compare these problems…
- What is one thing you can change (structure or function)?
- What can’t be changed?
- Tinker (tear things apart, play with everyday items)
- Be innovative with their goals and passions
- Community problem: Designing a space for a human
- Tools: Animoto, Scratch, Prezi, Minecraft, NovaLabs

5. Computational thinker
- Identify and order the sequential steps of a process
- Characterize phenomena by their component elements
- Identify causes leading to an event or from an event
- Break an event into problems and actions Cause and effect
- Examine the parts of a whole and their relationships
- Determine the similarities and differences
- Break into parts
- Computational thinking resources
Ideas:
- Plan an approach to a math problem
- Classify organisms in a new system
- Generalize qualities…
- Transfer what they learned to a new situation
- Find patterns/Make rules
Change a variable to find what happens - Breakdown a simple routing in 15 steps
- Create nodes and routes for an escape plan
- Animate a literary character
6. Creative communicator
Students communicate clearly and express themselves creatively for a variety of purposes using the platforms, tools, styles, formats and digital media appropriate to their goals.
- Write for different audiences
- Publish with purpose
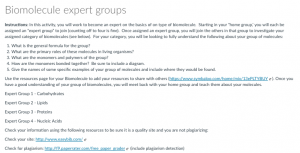
- Protein synthesis project
- Tools: Google Sites, Weebly, Wix, Twitter, Instagram, Seesaw, Blogger, Edublogs
7. Global collaborator
Students use digital tools to broaden their perspectives and enrich their learning by collaborating with others and working effectively in teams locally and globally.
- Build bridges with the world
- Find a common problem or issue that has perspective throughout the world
- Interdisciplinary learning
- Spark curiosity
- 7 steps to start a global collaboration project
- Global collaboration sites
- Tool: Periscope (free app that allows users to broadcast live video stream from anywhere in the world), SnagIt, Padlet, Twitter, ePals, Skype, Voxer, Hangouts, Seesaw
Generic question stems:
- Compare…and…with regards to…
- Describe in your own words
- Do you agree or disagree with this statement? What evidence is there to support your answer?
- Explain how…
- Explain why…
- How are…and…similar
- How could…be used to…?
- How does…affect…?
- How does…apply to everyday life?
- Summarize…in your own words.
- What are the implications of…?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of…?
- What do we already know about…?
- What do you think causes…? Why?
- What does ….mean?
- What is …analogous to?
- What is a counter-argument for…?
- What is a new example of…?
- What is another way to look at…?
- What is the best…and why?
- What is the difference between… and…?
- What is the meaning of…?
- What is the nature of…?
- What is the solution to the problem of…?
- What would happen if…?
- Why is …happening?
- Why is…important?
Supporting research
- https://www.iste.org/standards/standards/for-students
- https://www.k12blueprint.com/news/new-iste-standards-students
- https://edtechmagazine.com/k12/article/2017/06/iste-2017-new-standards-educators-focus-data-digital-citizenship
- https://edventures.com/blogs/stempower/transforming-learning-with-technology-new-iste-standards-for-students
- http://maculcommunity.org/iste-standards-students-groundwork-whats-possible-learning/
- https://www.coetail.com/bfullerton/2017/01/05/iste-standards-students/
- http://30hands.com/blog/digital-storytelling-and-iste-standards/
- https://behindmytechiewall.wordpress.com/2017/03/06/talking-tech-the-new-2016-iste-standards-for-students-2-of-8/
- http://www.jefcoed.com/academics/instructional_technology_data_security/i_s_t_e_standards
- https://www.orange.k12.nj.us/Page/13301
- http://schd.ws/hosted_files/cue2017nationalconference/2d/CUE2017_StudentStnds.pdf
- http://www.21things4teachers.net/21-things/1—basics/implementation/iste-standards-for-teachers-alignment/
- https://www.iste.org/explore/articleDetail?articleid=777&category=ISTE-Connects-blog&article=
- https://www.iste.org/explore/articleDetail?articleid=860&category=Set-the-standard&article=
- http://www.citejournal.org/volume-8/issue-4-08/social-studies/using-technology-as-a-tool-for-learning-and-developing-21st-century-citizenship-skills-an-examination-of-the-nets-and-technology-use-by-preservice-teachers-with-their-k-12-students/