Teacher Edition | View the Map
Week of March 19, 2023
Right click and SAVE AS
to download the Google Earth file for this episode
Use free Google Earth software
to OPEN it, using File> Open.
Find more tech info here.
St. Petersburg has over one million residents. Among all the world's cities with over one million residents, St. Petersburg is the furthest north. So I guess that makes this the COLDEST, highly populated city in the world? I assume St. Petersburg is farther north than New York City, Mexico City, or any of the other highly populated cities we have visited during our mission. Alena told us that her favorite month to visit her dad is in June. Right after she gets out of school, "White Nights" begin. Do you remember how Alaska had dark days without the sun? Well, St. Petersburg is similar. "White Nights" in June occur when the sun doesn't set until late evening (11 pm) and stays fairly light all night. Complete darkness doesn't occur for a few weeks. Alena said that St. Petersburg has a huge celebration called the "White Nights Festival." They have fireworks and everything to celebrate the end of the school year. Alena has a favorite place to visit in St. Petersburg - the Hermitage Museum. Alena took us on a "virtual tour" of the museum. This museum is VERY FAMOUS throughout the world. We included a link to the virtual tour - enjoy!
The summers in "Piter" are cool, short, and humid. The winters are long and cold, with a few warm spells. St. Petersburg is known as a transportation Hub. There are a ton of railroads that have St. Petersburg as their final destination or a connecting point for other locations. There are also several airports (the largest being Pulkovo International Airport). You can really get to anywhere in the world from this huge transportation center. We included the map from our last blog entry (can you find St. Petersburg?). We also included some pictures that Alena shared with us from her phone.
- Geo

Here is the Grand Cascade. This beautiful fountain area is a tourist attraction in St. Petersburg.

This picture shows the harbor in St. Petersburg. Isn't the lighthouse amazing!

This is the church that Alena and her father attend.
Map of Scandinavia
Here is the map we showed you in our last blog entry
Hermitage Museum
Take a virtual visit to the Hermitage Museum.
Airpano
Take a virtual tour of Saint Petersburg!
The climate in Sweden varies. The north experiences subarctic conditions. Do you remember what subarctic means? The climate in the south is temperate. The south has cold and cloudy winters and cool and partly cloudy summers. They don't have as many sunny days as we do in Phoenix. About 6% of the land in Sweden is arable. Some of the most common agricultural products include milk, wheat, barley, sugar beets, and meat.
Sweden has several natural resources - zinc, lead, copper, iron ore, arsenic, uranium, tungsten, timber, hydropower, and feldspar. Do you remember we learned about feldspar a few weeks ago? Do you remember what feldspar is?
The people of Sweden work in various industries to earn a living. Some of the more popular industries include motor vehicles, iron and steel, precision equipment (such as radio and telephone parts), processed foods, paper products, and several others. The main export from Sweden is machinery (35% of their total exports). Holy Idaho! That is over 1/3 of their total exports. I guess they can make machinery out of all the iron and steel. I wonder what exact type of machinery they are referring to? Most of the exports go to Germany, Norway, or the United States. Here are some pictures we took of Sweden.
- Meri

Look at this picture we found of the icicles in Sweden. It isn't as cold at this time of the year. I wish we could have seen the ice. Holy Idaho!

The waterfront of Stockholm.

This is a war monument that we saw. Geo loves visiting war monuments.
Visit Europe | 360-degree visit of Stockholm, Sweden
Here is one virtual tour we found - check it out!
This is another cool video VR tour - enjoy!
- Geo

The flag of Sweden

The streets of Stockholm (very narrow compared to the streets in our neighborhood).
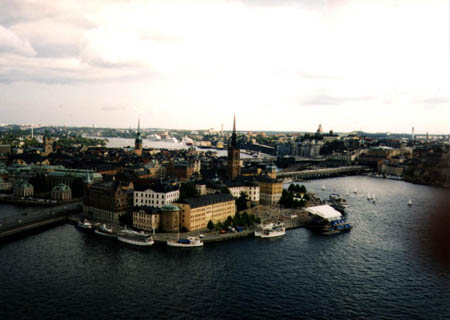
Another picture of the harbor area of Stockholm.
Map of France
Where do you think we should fly next? Should we go to Lyon, Paris, or Bordeaux?
arable - land that can be used to grow crops.
federal subject - similar to a state. It is a way that a country divides up the land into smaller governmental sections. Russia has 83 federal subjects.
federal subjects - similar to a state. It is a way that a country divides up the land into smaller governmental sections. Russia has 83 federal subjects.
Feldspar - group of minerals found in crystals. They are usually white, red, blue, or green.
latitude - the lines that run across (east and west) a map. Lines of latitude measure degrees via north or south. The equator is at 0 degrees latitude.
longitude - lines that run up and down the map (north and south). These lines are used to measure degrees east or west from the prime meridian. The prime meridian is located at 0 degrees longitude.
natural resources - any substance that is made by nature and used to enhance the lives of living things. Some examples of natural resources include sunlight, minerals, soil, and water.
State - land areas that are under the jurisdiction of a government.
Subarctic - a climate with comfortable summer months (never too hot), and extremely frigid winters.
temperate - a climate that provides warm summers and mild winters. The temperatures do not typically get extremely hot or cold.
Back to top
Grade 3-5: Knows the basic elements of maps and globes (title, legend, cardinal, scale, grid, meridians, time zones, etc.).
Grade 3-5: Uses map grids (e.g., latitude and longitude or alphanumeric system) to plot absolute location.
Grade 6-8: Understands concepts such as axis, seasons, rotation, and revolution.
Grade 3-5: Knows major physical and human features of places as they are represented on maps and globes. Knows how to read different maps: road, relief, globe, etc..
Grade 6-8: Knows the location of physical and human features on maps and globes (e.g., culture hearths such as Mesopotamia, Huang Ho, the Yucatan Peninsula, the Nile Valley; major ocean currents; wind patterns; land forms; climate regions).
Grade 6-8: Knows the relative location of, size of, and distances between places.
Grade 3-5: Understands how changing transportation and communication technology has affected relationships between locations. Ease of travel between some and difficulty getting to some others because of transportation and how people move and shop from one to the other because of the ease (trains, road systems, ferries, etc...).
Grade 3-5: Knows different methods to measure data (miles, kilometers, time, etc..).
Grade 6-8: Understands how places are connected and how these connections demonstrate interdependence and accessibility (such as - the role of the changing transportation and communication technology).
Grade 6-8: Knows the human characteristics of places (e.g., cultural characteristics such as religion, language, politics, technology, family structure, gender; population characteristics; land uses; levels of development).
Grade 3-5: Knows the characteristics of a variety of regions (climate, housing, religion, language, etc..).
Grade 6-8: Understands criteria that give a region identity (such as Amsterdam as a transportation center or the Sunbelt's warm climate and popularity with retired people).
Grade 3-5: Knows the physical components of Earth's atmosphere (weather and climate), lithosphere (land forms such as mountains), hydrosphere (oceans, lakes and rivers), and biosphere (vegetation and biomes).
Grade 3-5: Knows how Earth's position relative to the Sun affects events and conditions on Earth.
Grade 3-5: Knows how and why people divide Earth's surface into political and/or economic units (e.g., states in the United States and Mexico; provinces in Canada; countries in North and South America; countries linked in cooperative relationships, such as the European Union).
Grade 6-8: Understands the symbolic importance of capital cities (such as Canberra, a planned city, as the capital of Australia).
Grade 3-5: Knows how humans adapt to variations in the physical environment (e.g. choices of clothing, housing styles, agricultural practices, recreational activities, food, daily and seasonal patterns of life).
Grade 3-5: Knows how communities benefit from the physical environment (e.g., people make their living by farming on fertile land, fishing in local water, working in mines; the community is a port located on a natural harbor, a tourist center located in a scenic or historic area, an industrial center with good access to natural resources).